- Challenges and market environment
- Business model
- Strategy
- Our focus: Clearly Sustainable
- Material topics and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Governance structure
- Organisation
- Performance review
- col1
- Introduction to the performance review
- Customers and suppliers
- Finances
- Innovation and intellectual property
- Production and products
- Employees
- Environment
- Financial report
- col1
- At a glance
- Financial Report of the Vetropack Group
- Consolidated balance sheet
- Consolidated income statement
- Consolidated cash flow statement
- Changes in consolidated shareholders’ equity
- Consolidation principles
- Valuation principles
- Notes
- Ownership structure
- Company participations
- Report of the statutory auditor on the consolidated financial statements
- Five-year overview
- col2
- Financial Report of Vetropack Holding Ltd
- Balance sheet
- Income statement
- Notes
- Board of Directors’ (BoD) proposal for the corporate profit appropriation
- Report of the statutory auditor on the financial statements
- Five-year overview
- Corporate Governance
- col1
- Introduction
- Board of Directors
- Management Board
- Remuneration and additional information
- Shareholders’ participation rights
- Auditors
- Information policy
- Blocking period
- Contact address
- Remuneration report
- col1
- Introduction to the remuneration report
- Principles of the remuneration scheme and its components
- Organisation and authorities for determining remuneration
- Description of the remuneration components
- Board of Directors’ (BoD) remuneration
- Management Board’s remuneration
- Comparison of remuneration disbursed with remuneration approved by the Annual General Assembly
- Shareholdings
- Report of the statutory auditor on the remuneration report
- Sustainability report
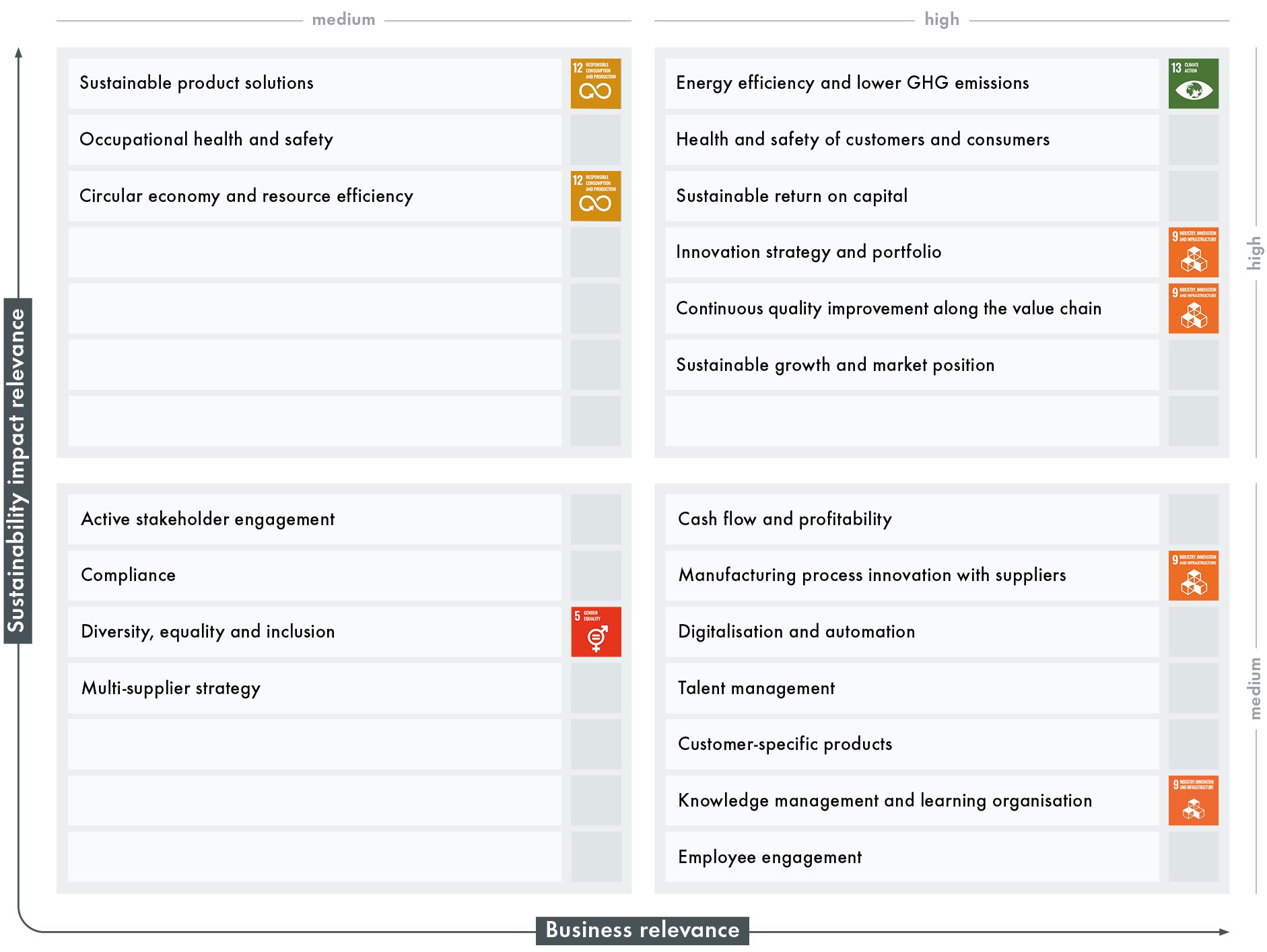
- The "outside-in" perspective: how relevant is a particular topic for Vetropack's long-term business success?
- The "inside-out" perspective: how strongly do business activities impact the company's context and environment – economy, people and ecology?
- 9.2: "Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and, by 2030, significantly raise industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product, in line with national circumstances, and double its share in least developed countries."
- 13.3: "Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning."
- 12.2: "By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources."
- 12.5: "By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse."
- 5.5: "Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making in political, economic and public life."
Foundations for success
Material topics and contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Definition of the key financial and non-financial topics
For the fourth time, Vetropack is reporting on the 2022 fiscal year in the form of an Integrated Annual Report which provides comprehensive information about our company’s financial and non-financial performance.
We structure the reporting and the material topics in accordance with the "six capitals" of integrated reporting (IR/IFRS):
Customers and suppliersFinancesInnovation and intellectual propertyProduction and productsEmployeesEnvironmentReappraisal of material topics
As part of its reporting process, Vetropack carries out an annual review of the materiality matrix developed in 2019. We undertook a full-scale reappraisal of the matrix's relevance in 2022. To ensure compliance with current statutory regulations (in the EU and Switzerland) and the provisions of the GRI Standards 2021, the "double materiality" concept was applied. This comprises two assessment perspectives:
Stakeholder relevance, as the third perspective for assessing materiality, was omitted due to changes in the requirements (as in the GRI Standards 2021).
Identifying and assessing impact
Vetropack updated its existing materiality analysis in autumn 2022. This was a multi-stage process: as the first step, a context analysis was used to identify additional, potentially material topics that would require assessment. We then identified the outward and inward impacts of these topics. This provided the basis for concise descriptions that include potential and actual impacts, both positive and negative, along the value chain. We then conducted an online survey to obtain internal stakeholders' assessments, which were consolidated and validated by management in a workshop.
Material topics adjusted and expanded
Customers and suppliers
Active stakeholder engagement (as previously)Multi-supplier strategy (as previously)Health and safety of customers and consumers (as previously)Finance
Cashflow and profitability
(previously together with «Sustainable return on capital»)Sustainable growth and market position (as previously)Sustainable return on capital
(previously together with «Cashflow and profitability»)Compliance (as previously)Innovation and intellectual property
Innovation strategy and portfolio (as previously)Manufacturing process innovations with suppliers
(previously «Process innovations with suppliers»)Production and products
Sustainable product solutions (as previously)Continuous quality improvement along the value chain (as previously)Digitalisation and automation (as previously)Customer-specific products (as previously)Employees
Talent management (as previously)Employee engagement (as previously)Knowledge management and learning organisation
(previously «Learning organisation»)Diversity, equality and inclusion (new)Occupational health and safety (as previously)Environment
Energy efficiency and lower GHG emissions
(previously «Energy efficiency and renewable energy» or separate material topics: «Minimising CO2 emissions, waste and water consumption» and «Climate-neutral logistics by 2030»)Circular economy and resource efficiency
(previously «Optimise use of raw materials»)Materiality matrix
Contribution to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs)
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations (UN) provide Vetropack with a reference system. This integrates the impact of our own business activities on the environment and society into the context of global sustainable development.
Following the reassessment of our materiality analysis, we reviewed our contribution to the SDGs. We focus here on four out of the seventeen SDGs where we see the greatest leverage for a significant contribution.
Contribution to SDG 9
Vetropack's strategic orientation is based on these core goals: create resilient infrastructure and build sustainable industrialisation. The company's investment programme will bring processes, plant and technologies into line with the latest state-of-the-art. This approach will support sustainable industrialisation. To achieve this, investment projects in the regions will foster and support a network of small companies around the plant. All plants in the Vetropack Group will benefit from the innovations and investments – and so will their partners throughout the value chain, and in the areas surrounding them.
Aspect that Vetropack can influence significantly
Material topics
Innovation strategy and portfolioContinuous quality improvement along the value chainManufacturing process innovation with suppliersKnowledge management and learning organisation
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
Contribution to SDG 13
As an industrial enterprise that operates internationally with a significant requirement for energy and resources, Vetropack has an ecological footprint. The company focuses its ecological commitment on climate protection.
Aspect that Vetropack can influence significantly
Material topics
Energy efficiency and lower GHG emissionsCircular economy and resource efficiency
Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
Contribution to SDG 12
The world's population currently consumes more resources than the ecosystems can provide. Moreover, consumption-based waste constitutes another formidable global problem. Glass has numerous properties that can contribute to more sustainable consumption. Achievable goals here are: less consumption of resources, less wastage of food, and less waste.
Aspect that Vetropack can influence significantly
Material topics
Sustainable product solutionsCircular economy and resource efficiency
Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
Contribution to SDG 5
Eliminating gender-specific differences is an obligatory requirement for a company that is committed to a comprehensively sustainable business policy. Moreover, gender equality has been proven to have positive effects on economic success, productivity, competitiveness and innovation intensity. Women have traditionally been in the minority in the glass industry, at all hierarchical levels and in all job profiles. Given this situation, Vetropack assesses the potential for improvement in this area as high.
Aspect that Vetropack can influence significantly
Material topic
Diversity, equality and inclusion
Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- col1
- col1
- Financial Report of Vetropack Holding Ltd
- col1
- col1